VMware vSphere Bitfusion accelerates ML and AI workloads
VMware's Bitfusion integration enhances vSphere's usage and utility with GPU virtualization to offload both ML and AI processing within VMware systems.
VMware vSphere Bitfusion virtualizes physical GPU hardware from ESXi hosts and aggregates them into a single pool of GPU resources.
VMware acquired Bitfusion in July 2019 and then integrated the software directly into VMware vSphere. VSphere Bitfusion offloads machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) processing in VMs and containers. The latest version of vSphere Bitfusion at time of publication is 2.5.
IT infrastructure must meet many requirements to operate vSphere Bitfusion. Once set up, Bitfusion can pool network-accessible GPU resources on hosts to share it among compute workloads. Virtualized GPU capacity can improve resource management, flexibility and accessibility.
A look at vSphere Bitfusion system requirements
Systems must meet specific requirements for a vSphere Bitfusion installation:
- installation of vSphere 7 with ESXi 7 hosts or higher;
- one and a half times more memory allocated for vSphere compared to the total physical RAM within the GPUs on the ESXi host; and
- a minimum of four virtual CPUs (vCPUs).
The Bitfusion network also has requirements:
- TCP/IP or Remote Direct Memory Access over Converged Ethernet, which is a protocol often used in Paravirtual RDMA (PVRDMA) adapters;
- bandwidth of 10 Gbps bandwidth for any VM that accesses two or more GPUs; and
- low latency -- below 50 microseconds -- with specific network device configurations, such as PVRDMA or Passthrough as seen in Figure 1.
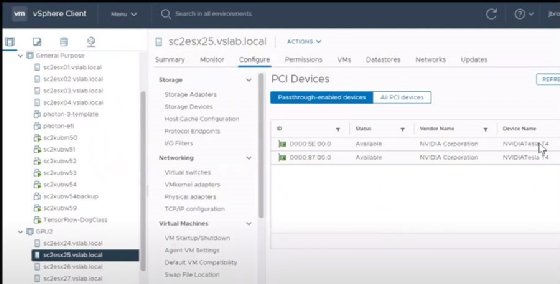
Finally, every Bitfusion server must connect to the same Network Time Protocol server.
Inside the vSphere Bitfusion architecture
VMware vSphere Bitfusion contains several components, including the vSphere Bitfusion client, Bitfusion cluster, Bitfusion Manager and Bitfusion Group.
Bitfusion client. VSphere installs and runs the Bitfusion client in each VM that executes AI and ML workloads. The Bitfusion client then sends and receives information between the server and the Bitfusion Manager. The Bitfusion client can run anywhere within a data center because the network connection follows the Bitfusion server to any location.
Bitfusion runs on Linux for both the client and server, but the Bitfusion client, specifically, only supports Linux distributions, such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux, CentOS and Ubuntu.
Bitfusion cluster. The Bitfusion cluster is a combination of all the Bitfusion servers and clients within vSphere. VSphere centrally manages the cluster via a standard vCenter server.
Bitfusion Manager. The Bitfusion Manager is the management tool that monitors the health, utilization, efficiency and availability of all GPU servers within the network via an admin UI. Admins also use the Bitfusion Manager to monitor GPU consumption, quotas and time limits.
Admins can access Bitfusion from vSphere's main menu when they connect vSphere via a vSphere client, as seen in Figure 2 below.
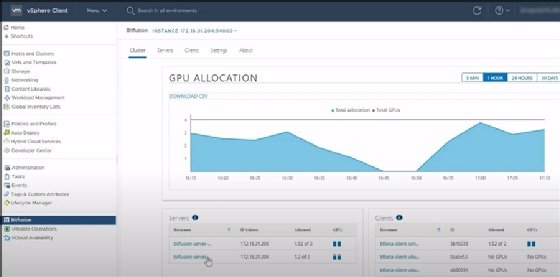
Figure 3 is a GPU cluster allocation chart that provides the allocation of GPUs with and without vSphere Bitfusion. It also provides a look at the number of GPUs within the cluster and number of GPUs allocated from the group.
Bitfusion Group. The Bitfusion client creates and installs the Bitfusion Group and uses the group to gather client resources.
VSphere Bitfusion benefits
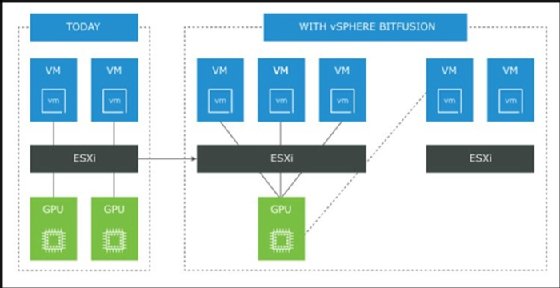
VMware vSphere Bitfusion makes it possible to virtualize physical GPU hardware from any number of ESXi hosts and aggregate them into a single GPU resource pool. A system can then assign full or partial GPU resources to specific applications. This setup is more flexible than if admins must exclusively allocate hardware to applications.
Still, vSphere Bitfusion requires physical GPUs, field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) or application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs).
VSphere Bitfusion enables VMs, as well as applications and workloads that run in containers, such as with Kubernetes, to consume elastic GPU resources. The vSphere Bitfusion integration also supports hybrid systems that run both VMs and containers simultaneously, similar to vSphere 7.
Bitfusion enhances vSphere usage and utility because admins have access to standard virtualization benefits, as well as virtualized graphics processor benefits for ML and AI applications.
VSphere Bitfusion use cases
GPU acceleration pays off for graphics-heavy workloads, but that's not the only use case. Various systems rely on AI and ML on a daily basis to perform operations. These workloads often require acceleration capabilities to perform successfully.
Bitfusion accomplishes hardware acceleration via GPU virtualization, which enables workloads to operate independently from the underlying hardware. There is also Bitfusion acceleration of FPGAs and ASICs for workloads in fields such as robotics and automotive vehicles.








